Week 9: Unbounded Media
what is unbounded media ?
No physical connection is required.
Space or air is the transmission medium for electromagnetic waves.
Source and destination can be static or mobile.
Broad spectrum from low to high bandwidth is available.
Can be quickly implemented.
Terrestial Microwave
- require line-of-sight transmission and reception microwave
- the taller the antennas, the longer the sight distance
- signals are propagate in one direction in a time
- consist of repeater which function to increase the distance-
They are two type of antenna
a) Parabolic Dish
- catching a wide range of waves and directing to a focus
-higher frequencies for higher data rates
-10-60 GHz
b) Horn
-looks like a gigantic scoop
-deflected the waves outward in a series of narrow parallel beams
-received transmission are collected by the scooped shape
Satellite microwave
The main problem with aero wave communication is the curvature of the earth,
mountains & other structure often block the line of side. Due to this
reason, many repeats are required for long distance which increases the cost of
data transmission between the two points. This problem is recommended by using
satellites.
Satellite micro wave transmission is used to transmit signals through out the
world. These system use satellites in orbit about 50,000 Km above the earth.
Satellite dishes are used to send the signals to the satellite where it is
again send back down to the receiver satellite. These transmissions also use
directional parabolic antenna’ with in line of side.
In satellite communication micro wave signals at 6 GHz is transmitted from a
transmitter on the earth through the satellite position in space. By the time
signal reaches the satellites becomes weaker due to 50,000 Km distance. The
satellite amplifies week signals and transmits it back to the earth at the
frequency less than 6 GHz.
The difference between 3g and 4g
3G is currently the world’s best connection method when it comes to
mobile phones, and especially mobile Internet. 3G stands for 3rd
generation as it is just that in terms of the evolutionary path of the
mobile phone industry. 4G means 4th generation. This is a set of
standard that is being developed as a future successor of 3G in the very
near future.
The biggest difference between the two is in the existence of compliant
technologies. There are a bunch of technologies that fall under 3G,
including WCDMA, EV-DO, and HSPA among others. Although a lot of mobile
phone companies are quick to dub their technologies as 4G, such as LTE,
WiMax, and UMB, none of these are actually compliant to the
specifications set forth by the 4G standard. These technologies are
often referred to as Pre-4G or 3.9G.
4G speeds are meant to exceed that of 3G. Current 3G speeds are topped
out at 14Mbps downlink and 5.8Mbps uplink. To be able to qualify as a 4G
technology, speeds of up to 100Mbps must be reached for a moving user
and 1Gbps for a stationary user. So far, these speeds are only reachable
with wired LANs.
Another key change in 4G is the abandonment of circuit switching. 3G
technologies use a hybrid of circuit switching and packet switching.
Circuit switching is a very old technology that has been used
in telephone systems for a very long time. The downside to this
technology is that it ties up the resource for as long as the connection
is kept up. Packet switching is a technology that is very prevalent in computer networks but has since appeared in mobile phones as well. With packet switching, resources are only used when there is information to
be sent across. The efficiency of packet switching allows the mobile
phone company to squeeze more conversations into the same bandwidth. 4G
technologies would no longer utilize circuit switching even for voice calls and video calls. All information that is passed around would be packet switched to enhance efficiency.
so we can conclude that -
1. 3G technologies are in widespread use while 4G compliant technologies are still in the horizon
2. 4G speeds are much faster compared to 3G
3. 3G is a mix of circuit and packet switching network while 4G is only a packet switching network
Week 8
Wi-Fi Wireless Antennas
Wi-Fi wireless networking works by
sending radio transmissions on specific frequencies where listening devices can
receive them. The necessary radio transmitters and receivers are built into
Wi-Fi enabled equipment like routers, laptops and phones.
Antennas are also key components of these radio communication systems, picking
up incoming signals or radiating outgoing Wi-Fi signals. Some Wi-Fi antennas,
particularly on routers, may be mounted externally while others are embedded
inside the device's hardware enclosure.

Antenna Power Gain
The connection range of a Wi-Fi device depends greatly on its antenna's
power gain. A numeric quantity measured in relative decibels (dB), gain
represents the maximum effectiveness of an antenna compared to a standard
reference antenna. Industry manufacturers use one of two different standards when
quoting gain measures for radio antennas:
dBi - decibels relative to an isotropic reference antenna
dBd - decibels relative to a dipole reference antenna
Most Wi-Fi antennas have dBi as their standard measure rather than dBd.
Dipole reference antennas work at 2.14 dBi that corresponds to 0 dBd. Higher
values of gain indicate an antenna capable of working at higher levels of
power, which usually results in greater range.
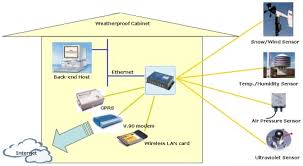
Definition: Satellite Internet
Satellite Internet is a form of high-speed Internet service. Satellite
Internet services utilize telecommunications satellites in Earth orbit to
provide Internet access to consumers.
Satellite Internet service covers areas where DSL and cable access is
unavailable. Satellite offers less network bandwidth compared to DSL or cable,
however. In addition, the long delays required to transmit data between the
satellite and the ground stations tend to create high network latency, causing
a sluggish performance experience in some cases. Network applications like VPN
and online gaming may not function properly over satellite Internet connections
due to these latency issues.
Wifi.
The name of a popular wireless networking technology that uses radio
waves to provide wireless high-speed Internet and network connections.
Initially, Wi-Fi was used in place of only the 2.4GHz 802.11b standard,
however the Wi-Fi Alliance has expanded the generic use of the Wi-Fi term to
include any type of network or WLAN product based on any of the 802.11
standards, including 802.11b, 802.11a, dual-band, and so on, in an attempt to
stop confusion about wireless LAN interoperability.
2G Networks
As of mid 2009, the majority GPS (Global System for Mobile or Groupe
Speciale Mobile) and CDMA mobile telephones in the United States operated on
the 2G network. 2G is an acronym which means "second generation." 2G
phones use a digital signal transmitted from radio transmission towers, as
opposed to 1G mobile phones, which used analog signals. Although 2G phones have
greater data transmission capabilities than 1G phones, the capacity is limited.
3G Networks
Among the newest network technology for mobile phones is the 3G network.
3G is an acronym which stands for "third generation." 3G telephones
work on both the GSM and CDMA networks. 3G technology features very fast
transmission of the mobile signal, which vastly expands the data transmission
capabilities of phones which run on 3G networks.
3G Network Advantages
The lightning-fast data transmission capabilities of 3G opens up a world
of features for cell phones which operate on 3G networks. This includes
streaming video and much faster uploads and downloads. Other features vary by
the particular model of the mobile phone. For instance, the 3G iPhone features
GPS (Global Positioning System) capabililities, where the 2G model does not.
3G Network Disadvantages
The major disadvantage for 3G network plans centers around pricing.
Generally, 3G network price points are much higher than 2G networks with
comparable features. In addition, the allowed minutes are often set at a much
lower threshold than for 2G plans of a similar price range.
Celullar Network

A cellular network is a radio network distributed over land areas called
cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, known as a cell
site or base station. When joined together these cells provide radio coverage
over a wide geographic area. This enables a large number of portable
transceivers (e.g., mobile phones, pagers, etc.) to communicate with each other
and with fixed transceivers and telephones anywhere in the network, via base
stations, even if some of the transceivers are moving through more than one
cell during transmission.
- Cellular networks offer a number of advantages over alternative
solutions.
flexible enough to use the features and
functions of almost all public and private networks.
- increased capacity
- reduced power use
- larger coverage area
- reduced interference from other signals

Horn Antenna
A horn antenna is used for the transmission
and reception of microwave signals. It derives its name from the characteristic
flared appearance. The flared portion can be square, rectangular, or conical.
The maximum radiation and response corresponds with the axis of the horn. In
this respect, the antenna resembles an acoustic horn. It is usually fed with a
wave guide.
Week 7
(CABLING)
LAN Techonology Cabling :

UTP stands for Unshielded
Twisted Pair cable. UTP cable is a 100 ohm copper cable that consists of 2 to
1800 unshielded twisted pairs surrounded by an outer jacket. They have no
metallic shield. This makes the cable small in diameter but unprotected against
electrical interference. The twist helps to improve its immunity to electrical
noise and EMI.
Category
Grade
Business Application
Frequency Range
Category 1
voice
grade
voice-grade
telephone networks only; not for data transmissions
750
kHz
Category 2
voice
grade
voice-grade
telephone networks, as well as IBM dumb-terminal connections to mainframe
computers
1
MHz
Category 3
data
grade
voice-grade
telephone networks, 10Mbps Ethernet, 4Mbps Token Ring, 100BaseT4 Fast
Ethernet, and 100VG Any LAN
16
MHz
Category 4
data
grade
16Mbps
Token Ring networks
20
MHz
Category 5
data
grade
100BastTX
Fast Ethernet, SONET, and OC-3 ATM networks
100
MHz
Category 5e
data
grade
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) Ethernet
100
MHz
Category 6
data
grade
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) Ethernet
250
MHz
Category 6A
data
grade
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) and 10 Gigabit Ethernet
500
MHz
Twisted Pair
Cables: This cable has two copper wires. Both these wires are twisted
around each other. The major purpose of twisting is to control the electrical
noise. These cables are very cheap. These can be used for both digital as well
as analog signal transmissions. But these cables have a limitation that these
can’t carry the signals to long distances. Signal becomes weak with the
increase in distance.
Parallel wire lines
Coaxial Cable

Fiber Optics
A technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
Fiber optics has several advantages over traditional metal communications lines
:
Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth than metal cables. This means that they can carry more data.
WEEK 6~ network topology
Study of the
arrangement or mapping of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a network, especially
the physical (real) and logical(virtual) interconnections between nodes

Physical topology:
Any given node in
the LAN will have one or more links to one or more other nodes in the network
and the mapping of these links and nodes onto a graph results in a geometrical
shape that determines the physical topology of the network

Logical Topology :
the mapping of the
flow of data between the nodes in the network determines the logical topology
of the network.
LINEAR BUS

-A linear bus
topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end.
STAR

-A star topology is
designed with each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected
directly to a central network hub or concentrator .
STAR-WIRED RING

-A star-wired
topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology.
TREE
-A tree topology
combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies.
MESH

Mesh topologies
involve the concept of routes. Unlike each of the previous topologies, messages
sent on a mesh network can take any of several possible paths from source to
destination. (Recall that even in a ring, although two cable paths exist,
messages can only travel in one direction.) Some WANs, most notably the
Internet, employ mesh routing.
Hybrid;

Hybrid networks use
a combination of any two or more topologies in such a way that the resulting
network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies (e.g., bus, star, ring,
etc.). For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is still a tree
network topology. A hybrid topology is always produced when two different basic
network topologies are connected. Two common examples for Hybrid network are:
star ring network andstar bus network.
Daisy chain;
Except for
star-based networks, the easiest way to add more computers into a network is by
daisy-chaining, or connecting each computer in series to the next. If a message
is intended for a computer partway down the line, each system bounces it along
in sequence until it reaches the destination. A daisy-chained network can take
two basic forms: linear and ring.
Week5 : network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer or biological network.Network topologies may be physical or logical.
There are several basic types of topology in networks:

(1) BUS TOPOLOGY
A linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end. All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.Ethernet and LocalTalk networks use a linear bus topology.The bus cable carries the transmitted message along the cable. As the message arrives at each workstation, the workstation computer checks the destination address contained in the message to see if it matches it's own. If the address does not match, the workstation does nothing more. If the workstation address matches that contained in the message, the workstation processes the message. The message is transmitted along the cable and is visible to all computers connected to that cable.
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
· Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus.
Disadvantages
· Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.

(2) STAR TOPOLOGY
A star topology is designed with each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub or concentrator. Data on a star network passes through the hub or concentrator before continuing to its destination. The hub or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow.This configuration is common with twisted pair cable; however, it can also be used with coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.The protocols used with star configurations are usually Ethernet or LocalTalk.
Advantages
Disadvantages
(3) STAR-WIRED
A star-wired topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology. Internally, the MAU (multistation access unit) of a star-wired ring contains wiring that allows information to pass from one device to another in a circle or ring. The Token Ring protocol uses a star-wired topology.

(4) TREE TOPOLOGY
A tree topology combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies.It consists of groups of star-configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Tree topologies allow for the expansion of an existing network, and enable schools to configure a network to meet their needs.
Advantage
· Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantages
· Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used.
(5) ETHERNET

Ethernet is the most widely-installed local area network ( LAN) technology. Specified in a standard, IEEE 802.3, Ethernet was originally developed by Xerox from an earlier specification called Alohanet (for the Palo Alto Research Center Aloha network) and then developed further by Xerox, DEC, and Intel. An Ethernet LAN typically uses coaxial cable or special grades of twisted pair wires. Ethernet is also used in wireless ethernet cables

(6) LOCALTALK
WEEK4:

A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information. Where at least one process in one device is able to send/receive data to/from at least one process residing in a remote device, then the two devices are said to be in a network.
Networks may be classified according to a wide variety of characteristics such as the medium used to transport the data, communications protocol used, scale, topology, and organizational scope.
Communications protocols define the rules and data formats for exchanging information in a computer network, and provide the basis for network programming. Well-known communications protocols are Ethernet, a hardware and Link Layer standard that is ubiquitous in local area networks, and the Internet Protocol Suite, which defines a set of protocols for internetworking, i.e. for data communication between multiple networks, as well as host-to-host data transfer, and application-specific data transmission formats.
Computer networking is sometimes considered a sub-discipline of electrical engineering, telecommunications, computer science, information technology or computer engineering, since it relies upon the theoretical and practical application of these disciplines.

There are two types of networks:
Local Area Network: The Local Area Network is also referred as LAN. This system spans on a small area like a small office or home. The computer systems are linked with cables. In LAN system computers on the same site could be linked.
Wide Area Network: A Wide Area Network or WAN is a type of networking where a number of resources are installed across a large area such as multinational business. Through WAN offices in different countries can be interconnected. The best example of a WAN could be the Internet that is the largest network in the world. In WAN computer systems on different sites can be linked.
Computer Networking Components


The Computer Networking Components are those devices that mediate the data in a computer network. The Computer Networking Components are also referred as Networking Devices or Network Equipments.
The Computer Networking Components are the Inter Working Unit or Intermediate Systems. There are data terminal equipments of networking that are responsible for receiving or generating data.
Computer Networking is the well defined communication between various computer systems using the Computer Networking Components. There are two or more systems that are being networked. Sometimes networking is also done between a computer and other devices like printer, scanner etc. The Computer Networking Components connects these devices with the system.
Some of the Computer Networking Components are:


2.Gateway: This device is placed at the network node. Its function is to interface other network that uses protocols.

3.Bridge Networking Device: For connecting data link layer and multiple network segments the bridge is used.

4.Switch for Networking: to allocate the traffic from one network to certain destinations the Switches are used. It splits the network traffic to send it to different lines. There are also Multilayer Switches, which provides functionality at the higher protocol layers.

5.Hub: These are used for connecting multiple Ethernet segments and make them act like a single segment.
The other devices which are equally important for Computer Networking are Repeater, protocol converter, brouter, proxy, firewall, multiplexer, modem, ISDN terminal adapter, and line driver.
Week 3
Aslmkum..ok.mggu ni plk nk cerita pasal Data Transmission.. Apa yg sy fhm kat cni ialah penghantaran data adalah pemindahan data dari titik ke titik yang sering digambarkan sebagai isyarat elektro-magnetik ke atas fizikal titik ke titik. Contoh saluran itu adalah wayar tembaga, gentian optik , saluran komunikasi tanpa wayar (macam handfon la), dan media storan. Istilah inibiasanya merujuk kepada komunikasi digital (iaitu sedikit aliran digital), tetapi mungkin termasuk penghantaran data analog dan sebagainya. Nk crita ni pnjg ckit la..so slamat membaca..;-)
DATA TRANSMISSION
Data transmission is the transfer of data from point-to-point often represented as an electro-magnetic signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels, and storage media. The term usually refers to digital communications (i.e. digital bit stream), but may include analog data transmission as well.
Data transmission is a subset of the field of data communications, which also includes computer networking or computer communication applications and networking protocols, for example routing and switching.
Week 9: Unbounded Media
what is unbounded media ?
No physical connection is required.
Space or air is the transmission medium for electromagnetic waves.
Source and destination can be static or mobile.
Broad spectrum from low to high bandwidth is available.
Can be quickly implemented.
Terrestial Microwave
- require line-of-sight transmission and reception microwave
- the taller the antennas, the longer the sight distance
- signals are propagate in one direction in a time - consist of repeater which function to increase the distance
a) Parabolic Dish
- catching a wide range of waves and directing to a focus
-higher frequencies for higher data rates
-10-60 GHz
b) Horn
-looks like a gigantic scoop
-deflected the waves outward in a series of narrow parallel beams
-received transmission are collected by the scooped shape
Satellite microwave
The main problem with aero wave communication is the curvature of the earth, mountains & other structure often block the line of side. Due to this reason, many repeats are required for long distance which increases the cost of data transmission between the two points. This problem is recommended by using satellites.
Satellite micro wave transmission is used to transmit signals through out the world. These system use satellites in orbit about 50,000 Km above the earth. Satellite dishes are used to send the signals to the satellite where it is again send back down to the receiver satellite. These transmissions also use directional parabolic antenna’ with in line of side.
In satellite communication micro wave signals at 6 GHz is transmitted from a transmitter on the earth through the satellite position in space. By the time signal reaches the satellites becomes weaker due to 50,000 Km distance. The satellite amplifies week signals and transmits it back to the earth at the frequency less than 6 GHz.
The difference between 3g and 4g
3G is currently the world’s best connection method when it comes to
mobile phones, and especially mobile Internet. 3G stands for 3rd
generation as it is just that in terms of the evolutionary path of the
mobile phone industry. 4G means 4th generation. This is a set of
standard that is being developed as a future successor of 3G in the very
near future.
The biggest difference between the two is in the existence of compliant
technologies. There are a bunch of technologies that fall under 3G,
including WCDMA, EV-DO, and HSPA among others. Although a lot of mobile
phone companies are quick to dub their technologies as 4G, such as LTE,
WiMax, and UMB, none of these are actually compliant to the
specifications set forth by the 4G standard. These technologies are
often referred to as Pre-4G or 3.9G.
4G speeds are meant to exceed that of 3G. Current 3G speeds are topped
out at 14Mbps downlink and 5.8Mbps uplink. To be able to qualify as a 4G
technology, speeds of up to 100Mbps must be reached for a moving user
and 1Gbps for a stationary user. So far, these speeds are only reachable
with wired LANs.
Another key change in 4G is the abandonment of circuit switching. 3G
technologies use a hybrid of circuit switching and packet switching.
Circuit switching is a very old technology that has been used
in telephone systems for a very long time. The downside to this
technology is that it ties up the resource for as long as the connection
is kept up. Packet switching is a technology that is very prevalent in computer networks but has since appeared in mobile phones as well. With packet switching, resources are only used when there is information to
be sent across. The efficiency of packet switching allows the mobile
phone company to squeeze more conversations into the same bandwidth. 4G
technologies would no longer utilize circuit switching even for voice calls and video calls. All information that is passed around would be packet switched to enhance efficiency.
so we can conclude that -
1. 3G technologies are in widespread use while 4G compliant technologies are still in the horizon
2. 4G speeds are much faster compared to 3G
3. 3G is a mix of circuit and packet switching network while 4G is only a packet switching network
Week 8
Wi-Fi Wireless Antennas
Wi-Fi wireless networking works by
sending radio transmissions on specific frequencies where listening devices can
receive them. The necessary radio transmitters and receivers are built into
Wi-Fi enabled equipment like routers, laptops and phones.
Antennas are also key components of these radio communication systems, picking
up incoming signals or radiating outgoing Wi-Fi signals. Some Wi-Fi antennas,
particularly on routers, may be mounted externally while others are embedded
inside the device's hardware enclosure.
Antenna Power Gain
The connection range of a Wi-Fi device depends greatly on its antenna's
power gain. A numeric quantity measured in relative decibels (dB), gain
represents the maximum effectiveness of an antenna compared to a standard
reference antenna. Industry manufacturers use one of two different standards when
quoting gain measures for radio antennas:
dBi - decibels relative to an isotropic reference antenna
dBd - decibels relative to a dipole reference antenna
Most Wi-Fi antennas have dBi as their standard measure rather than dBd.
Dipole reference antennas work at 2.14 dBi that corresponds to 0 dBd. Higher
values of gain indicate an antenna capable of working at higher levels of
power, which usually results in greater range.
Definition: Satellite Internet
Satellite Internet is a form of high-speed Internet service. Satellite
Internet services utilize telecommunications satellites in Earth orbit to
provide Internet access to consumers.
Satellite Internet service covers areas where DSL and cable access is
unavailable. Satellite offers less network bandwidth compared to DSL or cable,
however. In addition, the long delays required to transmit data between the
satellite and the ground stations tend to create high network latency, causing
a sluggish performance experience in some cases. Network applications like VPN
and online gaming may not function properly over satellite Internet connections
due to these latency issues.
Wifi.
The name of a popular wireless networking technology that uses radio
waves to provide wireless high-speed Internet and network connections.
Initially, Wi-Fi was used in place of only the 2.4GHz 802.11b standard,
however the Wi-Fi Alliance has expanded the generic use of the Wi-Fi term to
include any type of network or WLAN product based on any of the 802.11
standards, including 802.11b, 802.11a, dual-band, and so on, in an attempt to
stop confusion about wireless LAN interoperability.
2G Networks
As of mid 2009, the majority GPS (Global System for Mobile or Groupe
Speciale Mobile) and CDMA mobile telephones in the United States operated on
the 2G network. 2G is an acronym which means "second generation." 2G
phones use a digital signal transmitted from radio transmission towers, as
opposed to 1G mobile phones, which used analog signals. Although 2G phones have
greater data transmission capabilities than 1G phones, the capacity is limited.
3G Networks
Among the newest network technology for mobile phones is the 3G network.
3G is an acronym which stands for "third generation." 3G telephones
work on both the GSM and CDMA networks. 3G technology features very fast
transmission of the mobile signal, which vastly expands the data transmission
capabilities of phones which run on 3G networks.
3G Network Advantages
The lightning-fast data transmission capabilities of 3G opens up a world
of features for cell phones which operate on 3G networks. This includes
streaming video and much faster uploads and downloads. Other features vary by
the particular model of the mobile phone. For instance, the 3G iPhone features
GPS (Global Positioning System) capabililities, where the 2G model does not.
3G Network Disadvantages
The major disadvantage for 3G network plans centers around pricing.
Generally, 3G network price points are much higher than 2G networks with
comparable features. In addition, the allowed minutes are often set at a much
lower threshold than for 2G plans of a similar price range.
Celullar Network
A cellular network is a radio network distributed over land areas called
cells, each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, known as a cell
site or base station. When joined together these cells provide radio coverage
over a wide geographic area. This enables a large number of portable
transceivers (e.g., mobile phones, pagers, etc.) to communicate with each other
and with fixed transceivers and telephones anywhere in the network, via base
stations, even if some of the transceivers are moving through more than one
cell during transmission.
- Cellular networks offer a number of advantages over alternative solutions. flexible enough to use the features and functions of almost all public and private networks.
- increased capacity
- reduced power use
- larger coverage area
- reduced interference from other signals
Horn Antenna
A horn antenna is used for the transmission
and reception of microwave signals. It derives its name from the characteristic
flared appearance. The flared portion can be square, rectangular, or conical.
The maximum radiation and response corresponds with the axis of the horn. In
this respect, the antenna resembles an acoustic horn. It is usually fed with a
wave guide.
Week 7
(CABLING)
LAN Techonology Cabling :
a) Cable is
the medium through which information usually moves from one network device to
another.
b)
Several types of cable are commonly used with LANs.
c)
In some cases,a network will utilize only one type of cable, other networks will
use a variety of cable types.
UTP stands for Unshielded
Twisted Pair cable. UTP cable is a 100 ohm copper cable that consists of 2 to
1800 unshielded twisted pairs surrounded by an outer jacket. They have no
metallic shield. This makes the cable small in diameter but unprotected against
electrical interference. The twist helps to improve its immunity to electrical
noise and EMI.
UTP CATEGORIES:
Category
|
Grade
|
Business Application
|
Frequency Range
|
Category 1
|
voice
grade
|
voice-grade
telephone networks only; not for data transmissions
|
750
kHz
|
Category 2
|
voice
grade
|
voice-grade
telephone networks, as well as IBM dumb-terminal connections to mainframe
computers
|
1
MHz
|
Category 3
|
data
grade
|
voice-grade
telephone networks, 10Mbps Ethernet, 4Mbps Token Ring, 100BaseT4 Fast
Ethernet, and 100VG Any LAN
|
16
MHz
|
Category 4
|
data
grade
|
16Mbps
Token Ring networks
|
20
MHz
|
Category 5
|
data
grade
|
100BastTX
Fast Ethernet, SONET, and OC-3 ATM networks
|
100
MHz
|
Category 5e
|
data
grade
|
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) Ethernet
|
100
MHz
|
Category 6
|
data
grade
|
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) Ethernet
|
250
MHz
|
Category 6A
|
data
grade
|
Gigabit
(1000Mbps) and 10 Gigabit Ethernet
|
500
MHz
|
Twisted Pair
Cables: This cable has two copper wires. Both these wires are twisted
around each other. The major purpose of twisting is to control the electrical
noise. These cables are very cheap. These can be used for both digital as well
as analog signal transmissions. But these cables have a limitation that these
can’t carry the signals to long distances. Signal becomes weak with the
increase in distance.
Parallel wire lines
As
compared to other communicating cables we have discussed above, co-axial cables
are the best.
Parallel wire lines: These wires look like black ribbons. These
are used for attaching antenna with a television receiver set. Both hard as
well as flexible conductors can be used in these wires. These are also known as
the balanced lines. The space adjustment between conductor and the insulator
depends upon the amount of the power to be passed.
Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable is called "coaxial" because it
includes one physicalchannel that carries the
signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical
channel, both running along the same axis. The outer channel serves as a
ground. Many of these cables or pairs of coaxial tubes can be placed in a single
outer sheathing and, with repeaters, can carry information for a great distance.
Fiber Optics
A technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
Fiber optics has several advantages over traditional metal communications lines
:
Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth than metal cables. This means that they can carry more data.
WEEK 6~ network topology
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
Study of the
arrangement or mapping of the elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a network, especially
the physical (real) and logical(virtual) interconnections between nodes
Physical topology:
Any given node in
the LAN will have one or more links to one or more other nodes in the network
and the mapping of these links and nodes onto a graph results in a geometrical
shape that determines the physical topology of the network
Logical Topology :
the mapping of the
flow of data between the nodes in the network determines the logical topology
of the network.
LINEAR BUS
-A linear bus
topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end.
-All nodes (file
server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.
-Ethernet and
LocalTalk networks use a linear bus topology.
STAR
-A star topology is
designed with each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected
directly to a central network hub or concentrator .
-This configuration
is common with twisted pair cable; however, it can also be used with coaxial
cable or fiber optic cable.
-The protocols used
with star configurations are usually Ethernet or LocalTalk
STAR-WIRED RING
-A star-wired
topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology.
-Internally, the
MAU (multistation access unit) of a star-wired ring contains wiring that allows
information to pass from one device to another in a circle or ring
-The Token Ring
protocol uses a star-wired topology.
TREE
-A tree topology
combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies.
-It consists of
groups of star-configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone
cable. Tree topologies allow for the expansion of an existing network, and
enable schools to configure a network to meet their needs.
MESH
Mesh topologies
involve the concept of routes. Unlike each of the previous topologies, messages
sent on a mesh network can take any of several possible paths from source to
destination. (Recall that even in a ring, although two cable paths exist,
messages can only travel in one direction.) Some WANs, most notably the
Internet, employ mesh routing.
A mesh network in
which every device connects to every other is called a full mesh. As shown in
the illustration below, partial mesh networks also exist in which some devices
connect only indirectly to others.
Hybrid;
Hybrid networks use
a combination of any two or more topologies in such a way that the resulting
network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies (e.g., bus, star, ring,
etc.). For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is still a tree
network topology. A hybrid topology is always produced when two different basic
network topologies are connected. Two common examples for Hybrid network are:
star ring network andstar bus network.
Daisy chain;
Except for
star-based networks, the easiest way to add more computers into a network is by
daisy-chaining, or connecting each computer in series to the next. If a message
is intended for a computer partway down the line, each system bounces it along
in sequence until it reaches the destination. A daisy-chained network can take
two basic forms: linear and ring.
Week5 : network topology
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnections of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer or biological network.Network topologies may be physical or logical.
There are several basic types of topology in networks:
(1) BUS TOPOLOGY
A linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end. All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.Ethernet and LocalTalk networks use a linear bus topology.The bus cable carries the transmitted message along the cable. As the message arrives at each workstation, the workstation computer checks the destination address contained in the message to see if it matches it's own. If the address does not match, the workstation does nothing more. If the workstation address matches that contained in the message, the workstation processes the message. The message is transmitted along the cable and is visible to all computers connected to that cable.
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
· Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus.
· Requires less cable length than a star topology.
Disadvantages
· Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.
· A faulty cable or workstation will take the entire LAN down
· terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable.
· Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down.
· Not meant to be used as a stand-alone solution in a large building.
(2) STAR TOPOLOGY
A star topology is designed with each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub or concentrator. Data on a star network passes through the hub or concentrator before continuing to its destination. The hub or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow.This configuration is common with twisted pair cable; however, it can also be used with coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.The protocols used with star configurations are usually Ethernet or LocalTalk.
Advantages
· Easy to install, and wire.
· Easy to add new workstations
· No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
· Any non-centralised failure will have very little effect on the network
· Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
· Centralized control Centralized network/hub monitoring
Disadvantages
· Requires more cable length than a linear topology.
· If the hub or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disabled.
· More expensive than linear bus topologies because of the cost of the concentrators.
(3) STAR-WIRED
A star-wired topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology. Internally, the MAU (multistation access unit) of a star-wired ring contains wiring that allows information to pass from one device to another in a circle or ring. The Token Ring protocol uses a star-wired topology.
(4) TREE TOPOLOGY
A tree topology combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies.It consists of groups of star-configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable. Tree topologies allow for the expansion of an existing network, and enable schools to configure a network to meet their needs.
Advantage
· Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantages
· Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used.
· if the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
· More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
(5) ETHERNET
Ethernet is the most widely-installed local area network ( LAN) technology. Specified in a standard, IEEE 802.3, Ethernet was originally developed by Xerox from an earlier specification called Alohanet (for the Palo Alto Research Center Aloha network) and then developed further by Xerox, DEC, and Intel. An Ethernet LAN typically uses coaxial cable or special grades of twisted pair wires. Ethernet is also used in wireless ethernet cables
(6) LOCALTALK
LocalTalk is a particular implementation of the physical layer of the AppleTalk networking system from Apple Computer. LocalTalk specifies a system of shielded twisted pair cabling, plugged into self-terminating transceivers, running at a rate of 230.4 kbit/s.CSMA/CA was implemented as a random multiple access method.
WEEK4:
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information. Where at least one process in one device is able to send/receive data to/from at least one process residing in a remote device, then the two devices are said to be in a network.
Networks may be classified according to a wide variety of characteristics such as the medium used to transport the data, communications protocol used, scale, topology, and organizational scope.
Communications protocols define the rules and data formats for exchanging information in a computer network, and provide the basis for network programming. Well-known communications protocols are Ethernet, a hardware and Link Layer standard that is ubiquitous in local area networks, and the Internet Protocol Suite, which defines a set of protocols for internetworking, i.e. for data communication between multiple networks, as well as host-to-host data transfer, and application-specific data transmission formats.
Computer networking is sometimes considered a sub-discipline of electrical engineering, telecommunications, computer science, information technology or computer engineering, since it relies upon the theoretical and practical application of these disciplines.
There are two types of networks:
Local Area Network: The Local Area Network is also referred as LAN. This system spans on a small area like a small office or home. The computer systems are linked with cables. In LAN system computers on the same site could be linked.
Wide Area Network: A Wide Area Network or WAN is a type of networking where a number of resources are installed across a large area such as multinational business. Through WAN offices in different countries can be interconnected. The best example of a WAN could be the Internet that is the largest network in the world. In WAN computer systems on different sites can be linked.
The Computer Networking Components are those devices that mediate the data in a computer network. The Computer Networking Components are also referred as Networking Devices or Network Equipments.
The Computer Networking Components are the Inter Working Unit or Intermediate Systems. There are data terminal equipments of networking that are responsible for receiving or generating data.
Computer Networking is the well defined communication between various computer systems using the Computer Networking Components. There are two or more systems that are being networked. Sometimes networking is also done between a computer and other devices like printer, scanner etc. The Computer Networking Components connects these devices with the system.
Some of the Computer Networking Components are:
1.Router: This networking device is specialized for determining the next networking point where the data packet is forwarded toward its destination. Different protocols can't be interfaced through a router.
2.Gateway: This device is placed at the network node. Its function is to interface other network that uses protocols.
3.Bridge Networking Device: For connecting data link layer and multiple network segments the bridge is used.
4.Switch for Networking: to allocate the traffic from one network to certain destinations the Switches are used. It splits the network traffic to send it to different lines. There are also Multilayer Switches, which provides functionality at the higher protocol layers.
5.Hub: These are used for connecting multiple Ethernet segments and make them act like a single segment.
The other devices which are equally important for Computer Networking are Repeater, protocol converter, brouter, proxy, firewall, multiplexer, modem, ISDN terminal adapter, and line driver.
Week 3
Data transmission is the transfer of data from point-to-point often represented as an electro-magnetic signal over a physical point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibers, wireless communication channels, and storage media. The term usually refers to digital communications (i.e. digital bit stream), but may include analog data transmission as well.
Data transmission is a subset of the field of data communications, which also includes computer networking or computer communication applications and networking protocols, for example routing and switching.
Data transmission medium
In order for data transmission to occur, there must be a transmission line, also called transmission channel or channel, between the two machines.
These transmission channels are made up of several segments that allow the data to circulate in the form of electromagnetic, electrical, light or even acoustic waves. So, in fact, it is a vibratory phenomenon that is propagated over the physical medium.
Encoding of transmission signals
In order for data to be exchanged, an encoding must be chosen for the transmission signals. This depends basically on the physical medium used to transfer the data, the guaranteed data integrity and transmission speed.
Simultaneous data transmission
Data transmission is called "simple" if there are only two machines communicating, or if only a single piece of data is sent. Otherwise, it is necessary to install several transmission lines or to share the line among several different communication actors.
Communication protocols
A protocol is a common language used by all actors in the communication to exchange data. However, its role does not stop there. A protocol also allows:
- Initiation of communications
- Data exchange
- Error detection
- A "courteous" end of communications
Analog at a glance
As a technology, analog is the process of taking an audio or video signal (in most cases, the human voice) and translating it into electronic pulses. Digital on the other hand is breaking the signal into a binary format where the audio or video data is represented by a series of "1"s and "0"s. Simple enough when it's the device—analog or digital phone, fax, modem, or likewise—that does all the converting for you.
Is one technology better than the other? Analog technology has been around for decades. It's not that complicated a concept and it's fairly inexpensive to use. That's why we can buy a $20 telephone or watch a few TV stations with the use of a well-placed antenna. The trouble is, analog signals have size limitations as to how much data they can carry. So with our $20 phones and inexpensive TVs, we only get so much.
Enter digital
The newer of the two, digital technology breaks your voice (or television) signal into binary code—a series of 1s and 0s—transfers it to the other end where another device (phone, modem or TV) takes all the numbers and reassembles them into the original signal. The beauty of digital is that it knows what it should be when it reaches the end of the transmission. That way, it can correct any errors that may have occurred in the data transfer. What does all that mean to you? Clarity. In most cases, you'll get distortion-free conversations and clearer TV pictures.
You'll get more, too. The nature of digital technology allows it to cram lots of those 1s and 0s together into the same space an analog signal uses. Like your button-rich phone at work or your 200-plus digital cable service, that means more features can be crammed into the digital signal.
Compare your simple home phone with the one you may have at the office. At home you have mute, redial, and maybe a few speed-dial buttons. Your phone at work is loaded with function keys, call transfer buttons, and even voice mail. Now, before audiophiles start yelling at me through their PC screens, yes, analog can deliver better sound quality than digital…for now. Digital offers better clarity, but analog gives you richer quality.
But like any new technology, digital has a few shortcomings. Since devices are constantly translating, coding, and reassembling your voice, you won't get the same rich sound quality as you do with analog. And for now, digital is still relatively expensive. But slowly, digital—like the VCR or the CD—is coming down in cost and coming out in everything from cell phones to satellite dishes.
When you're shopping in the telecom world, you often see products touted as "all digital." Or warnings such as "analog lines only." What does it mean? The basic analog and digital technologies vary a bit in definition depending on how they're implemented.
Week 2:
What is Browser???
A browser is an application program that provides a way to look at and interact with all the information on the World Wide Web. The word "browser" seems to have originated prior to the Web as a generic term for user interfaces that let you browse (navigate through and read) text files online.
Technically, a Web browser is a client program that uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to make requests of Web servers throughout the Internet on behalf of the browser user. Most browsers support e-mail and the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) but a Web browser is not required for those Internet protocols and more specialized client programs are more popular.
The first Web browser, called WorldWideWeb, was created in 1990. That browser's name was changed to Nexus to avoid confusion with the developing information space known as the World Wide Web. The first Web browser with a graphical user interface was Mosaic, which appeared in 1993. Many of the user interface features in Mosaic went into Nescane Navigator. Microsoft followed with its Internet Explorer (IE).
As of September 2006, Internet Explorer is the most commonly used browser, having won the so-called browser wars between IE and Netscape. Other browsers include:
· Firefox, which was developed from Mozilla(the open sourse version of Netscape).
· Flock, an open source browser based on Firefox and optimized for Web 2.0 features such as blogging and social book making.
· Safari, a browser for Apple computers (at this writing, the third most popular browser).
· Lynx, a text-only browser for UNIX shell and VMS users.
· Opera, a fast and stable browser that's compatible with most relatively operating systems.
Directory
A directory is another name for a folder. Files on your hard disk are organized into various folders, or directories, so that it is easier to keep track of them. For example, you may keep your pictures in one folder and your music files in another folder. Folders can also contain other folders, allowing for more specific organization.
Since you can have folders within a folder, files on your hard drive are organized much like branches on a tree. The main directory on your hard drive is appropriately called the "root directory." Folders that exist within the root directory most likely contain other folders, which may branch out to even more folders.
When you are browsing one directory and want to open the folder that contains the current directory, it is called "moving up a directory." As you move up directories, you will eventually move up to the root directory. In Windows, this may be your C:\ directory, while on the Mac it will be the name of your hard drive, such as "Macintosh HD."
Meta Search Engine
Meta search engines are search engines that search other search engines. Confused? To put it simply, a meta search engine submits your query to several other search engines and returns a summary of the results. Therefore, the search results you receive are an aggregate result of multiple searches.
While this strategy gives your search a broader scope than searching a single search engine, the results are not always better. This is because the meta search engine must use its own algorithm to choose the best results from multiple search engines. Often, the results returned by a meta search engine are not as relevant as those returned by a standard search engine.

Clear History
Clear History is free and powerfull windows desktop application to clean search history from your computer. It is full featured program that greatly surpasses most commercial programs out there.
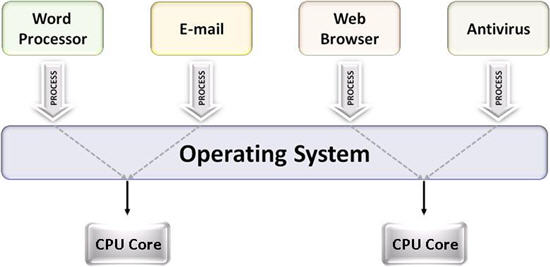
Multitasking
The ability to execute more than one task at the same time, a task being a program. The terms multitasking and multiprocessing are often used interchangeably, although multiprocessing implies that more than one CPU is involved.
In multitasking, only one CPU is involved, but it switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives the appearance of executing all of the programs at the same time.
There are two basic types of multitasking: preemptive and cooperative. In preemptive multitasking, the operating system parcels out CPU time slices to each program. In cooperative multitasking, each program can control the CPU for as long as it needs it. If a program is not using the CPU, however, it can allow another program to use it temporarily. OS/2, Windows 95, Windows NT, the Amiga operating system and UNIX use preemptive multitasking, whereas Microsoft Windows 3.x and the MultiFinder (for Macintosh computers) use cooperative multitasking.

Plug-in
Though software plug-ins might not make your room smell as nice as the scented ones you stick in an outlet, they are still useful. A software plug-in is an add-on for a program that adds functionality to it. For example, a Photoshop plug-in (such as Eye Candy) may add extra filters that you can use to manipulate images. A browser plug-in (such as Macromedia Flash or Apple QuickTime) allows you to play certain multimedia files within your Web browser. VST plug-ins add effects for audio recording and sequencing programs such as Cubase and Logic Audio.
Most graphics and audio programs today support plug-ins since they are a convenient way to expand the capabilities of the program. Though some plug-ins may be shipped with the program, most are developed by third-parties and are sold separately. Because companies that make browser plug-ins are often competing for a standard (such as Flash and QuickTime), these plug-ins are usually available as free downloads from the Internet.
Assalammuallaikum..utk mggu kedua ni plk..psl Introduction To Telecommunication..ni cite psl ape itu telekomunikasi, mcm mane komunikasi tu berlaku dan lain2 la..so slmt membaca...;-)
Week 1: Introduction To Telecommunication

What is communication
Communication is simply the imparting, conveying or exchange of thoughts, messages, ideas, knowledge or information by sign and sound like speech, signals, writing, or behavior.
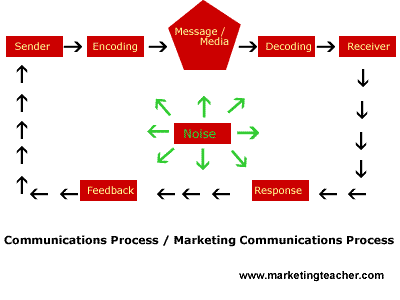
Diagram 1.1: The communication process
What is telecommunication
Telecommunication refers to communication over long distances, covers all forms of distance and conversion of the original communication, including radio, telegraphy, television, telephony, data communication and computer networking. It also can be define as process of transmitting or receiving information over a distance by any electrical or electromagnetic medium. The information may take the form of voice, video, or data.
Communications Technology Timeline:
Elements of a Computer and Communication System
Hardware
Hardware is the most obvious part of a computer-based information system. Hardware refers to the computers themselves, along with any and all peripherals, including servers, routers, monitors, printers and storage devices.
Software
Without software, the hardware wouldn't be very useful. Software is what tells the hardware how to function. It gathers, organizes and manipulates data and carries out instructions. Everything you do using a computer is done by the software.
Data
Data, or information is the information part of an information system, and whether that is statistical data, sets of instructions, lists of names or even graphics and animations
Procedures
It is commonly said that "procedures are to people what software is to hardware." Procedures are the rules, descriptions and instructions for how things are done. In computer-based information systems, procedures are frequently covered in instruction or user manuals that describe how to use the hardware, software and data.
People
People are the most often overlooked and most important part of a computer-based information system. It is people who design and operate the software, input the data, build the hardware and keep it running.
Communication
The components that allow one computer to communicate with another are hardware and are controlled by software. If communication between people is included in this element, though, it is an important element
Assalammualaikum...utk minggu pertama ni, aku baru blaja buat blog..so mybe ni agak simple laa..insyaAllah..aku akan update lg dengan nota n tambah2 ckit pkra2 yg agak mnarik utk korg tgk blog aku..hope korg follow la aku ea..hehe;-)
week 1
(INTRO)

what is communication??
The imparting,conveying or exchange of thoughts,messages,idea,knowledge or information by sign and sound like speech,writing or behavior.
how about telecommunication ??
Is refers to the transfer of data(communication)from a transmitter to a receiver across a distance
6 elements in computer&communication technology::
1.people
~ the most important element in communication because they built, analyse and develop the system.
2.procedure
~ specification of the series of actions, acts or operation which have to be executed in the same manner in order to obtain always the same result in the same circumstances example: emergency procedures.
3.data/information
~ information stored on the computer system, used by applications to accomplish tasks.
4.hardware
~ units for data:: Bit, Byte, Kilobyte(KB), Megabyte(MB), Gigabyte(GB), Terabyte(TB).
5.software
~ refers to parts of the computer that have no materials form: programs, data, protocols and others also called by software.
6.communication
~ transmission of data.
~ can conversion of data analog-to-digital, and digital-to-analog.
5 categories of ICT equipment/devices::
- input
-output
-process
-storage
-communication
woo...i know some about marketing communication process...In the past a number of terms have been used in the field of marketing
BalasPadamcommunications the most common of which appear to be ‘advertising’ and ‘promotion’.
gengsterjohor??!!!
BalasPadamhehe..ursula..sy gengster x??hehe
BalasPadamgangster sgtttt !!!!!hehehehe
BalasPadamheheheh...jeles la tu...haha
BalasPadam